Page 63 - Maths Class 06
P. 63
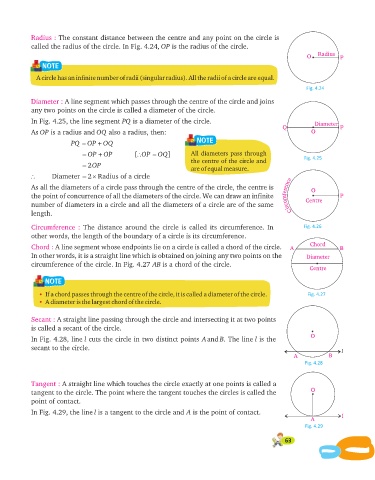
Radius : The constant distance between the centre and any point on the circle is
called the radius of the circle. In Fig. 4.24, OP is the radius of the circle.
Radius
O P
NOTE
A circle has an infinite number of radii (singular radius). All the radii of a circle are equal.
Fig. 4.24
Diameter : A line segment which passes through the centre of the circle and joins
any two points on the circle is called a diameter of the circle.
In Fig. 4.25, the line segment PQ is a diameter of the circle. Diameter
Q P
As OP is a radius and OQ also a radius, then: O
NOTE
PQ = OP + OQ
= OP + OP [\OP = OQ ] All diameters pass through
the centre of the circle and Fig. 4.25
= 2OP
are of equal measure.
\ Diameter = ´2 Radius of a circle
c e
As all the diameters of a circle pass through the centre of the circle, the centre is r e n O
the point of concurrence of all the diameters of the circle. We can draw an infinite e f m P
number of diameters in a circle and all the diameters of a circle are of the same u c r Centre
length. i C
Circumference : The distance around the circle is called its circumference. In Fig. 4.26
other words, the length of the boundary of a circle is its circumference.
Chord : A line segment whose endpoints lie on a circle is called a chord of the circle. A Chord B
In other words, it is a straight line which is obtained on joining any two points on the Diameter
circumference of the circle. In Fig. 4.27 AB is a chord of the circle.
Centre
NOTE
If a chord passes through the centre of the circle, it is called a diameter of the circle. Fig. 4.27
A diameter is the largest chord of the circle.
Secant : A straight line passing through the circle and intersecting it at two points
is called a secant of the circle.
O
In Fig. 4.28, line l cuts the circle in two distinct points Aand B. The line l is the
secant to the circle.
l
A B
Fig. 4.28
Tangent : A straight line which touches the circle exactly at one points is called a
tangent to the circle. The point where the tangent touches the circles is called the O
point of contact.
In Fig. 4.29, the line l is a tangent to the circle and A is the point of contact.
A l
Fig. 4.29
63