Page 58 - Maths Class 06
P. 58
D E C
K
G
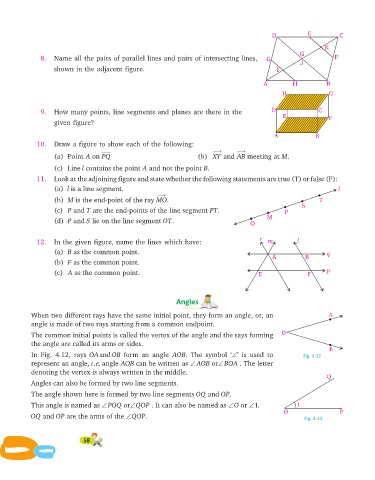
8. Name all the pairs of parallel lines and pairs of intersecting lines, G F
J
shown in the adjacent figure. I
A H B
H G
9. How many points, line segments and planes are there in the D C
E F
given figure?
A B
10. Draw a figure to show each of the following:
¾® ¾®
(a) Point A on PQ (b) XY and AB meeting at M.
(c) Line l contains the point A and not the point B.
11. Look at the adjoin ing figure and state whether the follow ing state ments are true (T) or false (F):
(a) l is a line segment. l
¾®
(b) M is the end-point of the ray MO. T
S
(c) P and T are the end-points of the line segment PT. P
M
(d) P and S lie on the line segment OT. O
r
12. In the given figure, name the lines which have: m l
(a) B as the common point. q
A B
(b) F as the common point.
(c) A as the common point. E F p
Angles
When two different rays have the same initial point, they form an angle, or, an A
angle is made of two rays starting from a common endpoint.
The common initial points is called the vertex of the angle and the rays forming O
the angle are called its arms or sides.
B
In Fig. 4.12, rays OAand OB form an angle AOB. The symbol ‘Ð’ is used to Fig. 4.12
represent an angle, i e. . angle AOB can be written as Ð AOB orÐBOA . The letter
denoting the vertex is always written in the middle.
Q
Angles can also be formed by two line segments.
The angle shown here is formed by two line segments OQ and OP.
This angle is named as ÐPOQ orÐQOP . It can also be named as ÐO or Ð1. l
O P
OQ and OP are the arms of the ÐQOP. Fig. 4.13
58