Page 77 - Maths Class 06
P. 77
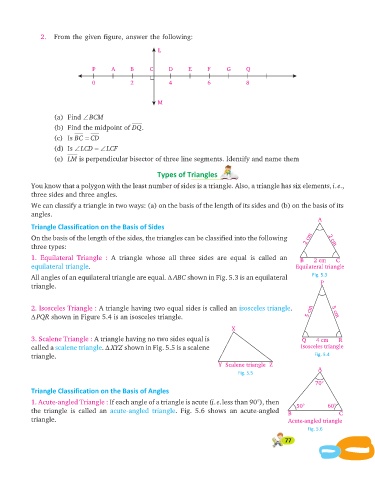
2. From the given figure, answer the following:
L
P A B C D E F G Q
0 2 4 6 8
M
(a) Find ÐBCM
(b) Find the midpoint of DQ.
(c) Is BC = CD
(d) Is ÐLCD = ÐLCF
(e) LM is perpendicular bisector of three line segments. Identify and name them
Types of Triangles
You know that a polygon with the least number of sides is a triangle. Also, a triangle has six elements, i e. .,
three sides and three angles.
We can classify a triangle in two ways: (a) on the basis of the length of its sides and (b) on the basis of its
angles.
A
Trian gle Clas si fi ca tion on the Basis of Sides
On the basis of the length of the sides, the triangles can be classified into the following 2 cm 2 cm
three types:
1. Equilateral Triangle : A triangle whose all three sides are equal is called an B 2 cm C
equilateral triangle. Equilateral triangle
All angles of an equilateral triangle are equal. D ABC shown in Fig. 5.3 is an equilateral Fig. 5.3
triangle. P
2. Isosceles Triangle : A triangle having two equal sides is called an isosceles triangle. 5 cm 5 cm
DPQR shown in Figure 5.4 is an isosceles triangle.
X
3. Scalene Triangle : A triangle having no two sides equal is Q 4 cm R
called a scalene triangle. D XYZ shown in Fig. 5.5 is a scalene Isosceles triangle
triangle. Fig. 5.4
Y Scalene triangle Z
A
Fig. 5.5
70°
Triangle Classification on the Basis of Angles
1. Acute-angled Triangle : If each angle of a triangle is acute (i e. . less than 90°), then
50° 60°
the triangle is called an acute-angled triangle. Fig. 5.6 shows an acute-angled B C
triangle. Acute-angled triangle
Fig. 5.6
77